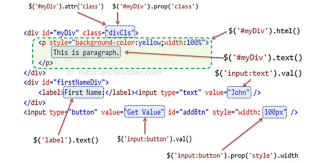
Textfield with Autocomplete
Autocomplete is implemented in Drupal through AJAX.
When users type into a textbox, code on the client page dynamically loads new data from the server (a Drupal website) and uses this data to update the user display (provide a drop-down list of matching options, which the user can select from).
read more inside, including code examples
Drush: how to Import and Export mySql database
Databases have the urge to grow, in some cases they are so big to manipulate, which means that import and export is imposible with the current tools like cPanel .
The Drush team created a tool which will help us to manipulate the database, which was defined in the settings configuration, regardless its size.
pay attention, most chance that import database will be available to files which ware created by export activity.
How to share Drupal content via Facebook with correct images
When you share a post of your drupal site on facebook, it will automatically detect the images of your node for you to choose.
But sometimes, it does not detect any images, or the detected images are not what you want.
You can always upload the main image manually. That's fine, because you are the owner of the site, you know which ones to choose. However, if your readers share that piece of content and it has an ugly image, it does not look attracting at all.
Display Forms in a Modal Dialog
Display create a node in a modal dialog
By default when creating a node, the save action will redirect the user to another page but if we want to just close the modal dialog and leave the user on the same page we need to tell the form to do that.
For this we are going to alter the form and add an AJAX command letting Drupal know that we want to close the dialog as soon as the node is created.
Code Snippet
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Ajax\AjaxResponse;
use Drupal\Core\Ajax\CloseModalDialogCommand;
use Drupal\Core\Ajax\RedirectCommand;
/**
* Implements hook_form_alter().
*/
function modal_form_example_form_node_article_form_alter(&$form, FormStateInterface $form_state, $form_id) {
$form['actions']['submit']['#submit'][] = '_modal_form_example_ajax_submit';
$form['actions']['submit']['#attributes']['class'][] = 'use-ajax-submit';
// in some cases this was needed:
// $form['#attached']['library'][] = 'core/jquery.form';
// $form['#attached']['library'][] = 'core/drupal.ajax';
}
/**
* Close the Modal and redirect the user to the homepage.
*
* @param array $form
* The form that will be altered.
* @param \Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface $form_state
* FormState Object.
*/
function _modal_form_example_ajax_submit(array $form, FormStateInterface &$form_state) {
$response = new AjaxResponse();
$response->addCommand(new CloseModalDialogCommand());
$form_state->setResponse($response);
}Drupal Form Element Reference
Drupal core provides a couple dozen different input #type elements that can be added to forms. This includes one for every standard HTML5 input element, and some Drupal-specific ones that encapsulate more complex interactions like uploading files. But how can you know what elements exist? Where do you find information about what Render API properties each element uses?
Composer 2.0 is now available
Massive improvements in terms of both speed and memory usage with new Composer.
The difference depends on your use case, so while I've seen reports of improvements of over 50% to both in some projects, I cannot put an exact number on it.
As a side note to this, require/remove and partial updates are now much faster because Composer will now only load the metadata of the packages which are being changed.
Drush Installation
Drush is a command line shell and Unix scripting interface for Drupal. Drush core ships with lots of useful commands for interacting with code like modules/themes/profiles. Similarly, it runs update.php, executes sql queries and DB migrations, and misc utilities like run cron or clear cache. Drush can be extended by 3rd party commandfiles.
How to keep your session data
Sometimes you need to temporarily store information per same user, which means handling his session data, in previous version of drupal it was easy and more like handling it in PHP programming, but with drupal 8, since the desire was to do everything in OOP strategy it changed.
This article will review some of the options to handle session date which are available on drupal8.
First lets remember how it was done with drupal7: using the $_SESSION in module file during the hooking implementation
In Drupal 8 there's two services to handle session data:
Custom Block: Create fast and simple
Blocks are individual pieces of your site’s web page layout. They are placed inside the regions of your theme, and can be created, removed, and rearranged in the Block layout (admin/structure/block) administration page.
Examples of blocks include the Who’s online listing, the main navigation menu, and the breadcrumb trail. The main page content is also a block.
Code Snippet
<?php
namespace Drupal\basic_module\Plugin\Block;
use Drupal\Core\Block\BlockBase;
/**
* Block annotation
*
* @Block(
* id = "basic_block",
* admin_label = @Translation("Basic Block"),
* )
*/
class BasicBlock extends BlockBase {
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public function build() {
$markup = '';
$markup .= '<div>';
$markup .= ' <p>Anything can come here: code, variables, html, etc. </p>' ;
$markup .= '</div>';
return [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => $markup,
];
}
} // end of classHow to prevent drupal to filter out style attribute from custom block code
When creating custom block, the inherit function build() return an element, usualy it include tag: #markup,
but it seems that it filter out the attributes, so how can we overwrite it correctly without the filter?
In other words we want to prevent drupal to filter out style attribute from custom block code
The '#markup' is filtered in ->ensureMarkupIsSafe(), which is called from within ->doRender().
The same does not apply to '#children' .
How to change an existing Drupal form
Changing an existing form is one of the first things that new Drupal developers will learn how to do.
It is a natural extension from site building, where you might need to change one thing on a form created by a core or contributed module.
One of the benefits of using the Form API to construct forms is that any module can alter any other module's form.
In this tutorial, you are going to learn how to alter a Drupal form.
Open Form in Modal mode also known as Pop-Up
Modal dialogs are incredibly useful on websites as they allow the user to do something without having to leave the web page they are on. Drupal 8 now has a Dialog API in core, which greatly reduces the amount of code you need to write to create a modal dialog. Dialogs in Drupal 8 leverage jQuery UI.
Creating a Block in Drupal 10 Programmatically
Drupal's great feature is Custom Block. blocks are easy and fast to set in any region, with Drupal9 you can even set the same block in a few regions.
There are a few technical options to create a block, here we will overview the programming option only.
so, what is a block?
Blocks are chunks of content with ID and classes which can be placed in manipulated within the page.
Code Snippet
namespace Drupal\my_module\Plugin\Block;
use Drupal\Core\Block\BlockBase;
use Drupal\Core\Block\BlockPluginInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Session\AccountInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Access\AccessResult;
use Drupal\Core\Cache\UncacheableDependencyTrait;
/**
* Provides a 'SetTask' Block.
*
* @Block(
* id = "dashboard_newtask_block",
* admin_label = @Translation("Dashboard New Task"),
* category = @Translation("DrupalVIP"),
* )
*/
class NewTaskBlock extends BlockBase implements BlockPluginInterface {
use UncacheableDependencyTrait;
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function build() {
// Do NOT cache a page with this block on it.
\Drupal::service('page_cache_kill_switch')->trigger();
// build from form
$build = \Drupal::formBuilder()->getForm('Drupal\drupalvip_dashboard\Form\NewTaskForm');
$build['#attributes']['class'][] = 'my_class';
$build['#cache']['max-age'] = 0;
$build['#cache']['contexts'] = [];
$build['#cache']['tags'] = [];
return $build;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function blockForm($form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$form = parent::blockForm($form, $form_state);
$config = $this->getConfiguration();
$form['block_note'] = [
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => $this->t('Note'),
'#description' => $this->t('block note '),
'#default_value' => isset($config['block_note']) ? $config['block_note'] : '',
];
return $form;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function blockSubmit($form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
parent::blockSubmit($form, $form_state);
$values = $form_state->getValues();
$this->configuration['block_note'] = $values['block_note'];
}
} // end of class
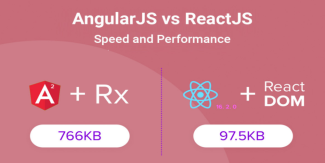
React vs Angular
What is React JS?
React is a Javascript library developed by Facebook which allows you to build UI components. It facilitates the creation of interactive User Interfaces. It also makes the code easier to understand and launch. React JavaScript framework uses server-side rendering to provide a flexible, performance-oriented solution.
AngularJS Vs ReactJS comparison
Web development teams across the world highly prefer AngularJS and ReactJS.
However, technical decision-makers, like project managers and development managers face the dilemma of choosing between the two.
As you will agree, every business has its unique development needs. Therefore, there is no standalone framework that would suit the varied development needs.
We’ve attempted to offer a detailed comparison to support the business processes.
Drupal Dictionary
This glossary describes terminology and acronyms used in the Drupal project and by the Drupal community.
This is a Drupal 9 version of the glossary, however, these terms are not (typically) specific to any version of Drupal.
We will add new terms and other terms which are from the web development industry.
If you feel that there is a term missing, please add it as a comment.
Drupal And React
Its time for a more powerful client-side with drupal, and we can do this with React
So, what is React and how can we integrate it with Drupal. I will try to answer both questions and more within this article.
React is a JavaScript library that makes it easy to create interactive user interfaces.
Drupal is a content management system (CMS) with a powerful web services API.