Form Element
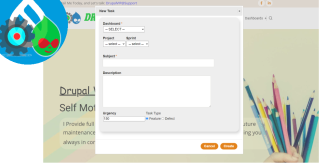
Displaying 1 - 9 of 9Select Element, its more hard to deal with Ajax
Drupal Form Select element is harder to deal with when desired to add to it Ajax activities
Ajax is a bit misleading, it's not all on the client side, and if we still want to handle it from the code which is located on the server, e/s program it with the form objects like $form & $form_state it still needs to update the server side within the flow, and the form is still need to have synchronization transactions between the client, server, and cache
not enough documentation on that, especially when working with specific elements like SELECT
Code Snippet
public function buildForm(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state, $dashboard = 0, $project=0, $sprint=0, $redirect='') { //
$config = \Drupal::config('drupalvip_task.settings');
$log = $config->get('log');
($log)? \Drupal::logger("drupalvip_task")->debug(__FUNCTION__ . ": START "):'';
($log)? \Drupal::logger("drupalvip_task")->debug("Form Args: da[$dashboard] pr[$project] sp[$sprint] rd[$redirect]"):'';
$form['redirect'] = array(
'#type' => 'value',
'#value' => $redirect,
);
//dashboard select
$dashboard_default = ($dashboard==0) ? null : $dashboard;
$dashboard_options = DashboardController::getDashboards();
$form['dashboard_select'] = [
'#type' => 'select',
'#title' => t('Dashboard'),
//'#name' => 'dashboard-select', <-- prevent the form_state to update
'#options' => $dashboard_options,
'#sort_options' => TRUE,
'#required' => TRUE,
'#empty_option' => "-- SELECT --",
'#size' => 1,
'#default_value' => $dashboard_default,
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['use-ajax'],
//'id' => "edit-dashboard-select", <-- this prevent the callback
],
'#ajax' => [
'callback' => '::submitFormDashboardSelected',
'wrapper' => 'group-select-wrapper',
'suppress_required_fields_validation' => TRUE,
],
];
$form['group'] = [
'#type' => 'fieldgroup',
'#prefix' => '<div id="group-select-wrapper">',
'#suffix' => '</div>',
];
$options[0] = "-- select --";
$form['group']['project_select'] = [
'#type' => 'select',
'#title' => $this->t('Project'),
'#options' => $options,
'#limit_validation_errors' => [],
//'#empty_option' => "-- select --",
'#size' => 1,
'#default_value' => 0,
];
if ($dashboard > 0) {
$project_options = DashboardController::getProjects($dashboard);
$project_options_2 = $options + $project_options ;
$form['group']['project_select']['#options'] = $project_options_2; //$project_options;
$form['group']['project_select']['#default_value'] = $project;
}
$form['group']['sprint_select'] = [
'#type' => 'select',
'#title' => $this->t('Sprint'),
'#options' => $options,
'#limit_validation_errors' => [],
//'#empty_option' => "-- select --",
'#size' => 1,
'#default_value' => 0,
];
if ($dashboard > 0) {
$sprint_options = DashboardController::getSprints($dashboard);
$sprint_options_2 = $options + $sprint_options ;
$form['group']['sprint_select']['#options'] = $sprint_options_2;
$form['group']['sprint_select']['#default_value'] = $sprint;
}
$form['subject'] = [
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => $this->t('Subject'),
'#required' => TRUE,
'#attributes' => [
//'id' => "task-subject-box",
],
];
$form['actions'] = [
'#type' => 'actions',
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['form_actions'],
],
];
$form['actions']['cancel'] = [
'#type' => 'submit',
'#value' => $this->t('Cancel'),
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['button','use-ajax','form-submit-modal','action-cancel' ],
],
'#ajax' => [
'callback' => [$this, 'submitFormClose'],
'event' => 'click',
],
];
$form['actions']['create'] = [
'#type' => 'submit',
'#value' => $this->t('Create'),
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['button','use-ajax','form-submit-modal','action-create' ],
],
'#ajax' => [
'callback' => [$this, 'submitFormCreate'],
'event' => 'click',
'onclick' => 'javascript:var s=this;setTimeout(function(){s.value="Saving...";s.disabled=true;},1);',
],
];
$form['#attributes']['class'][] = 'drupalvip_form';
$form['#attached']['library'][] = 'drupalvip_task/content';
$form['#attached']['library'][] = 'core/drupal.dialog.ajax';
$form['#attached']['library'][] = 'core/drupal.ajax';
$form['#attached']['library'][] = 'core/jquery.form';
($log)? \Drupal::logger("drupalvip_task")->debug(__FUNCTION__ . ": RETURN FORM "):'';
return $form;
}Form Element 'table' with TableDrag and TableSelect
Building and rendering a table required writing a custom/dedicated theme function for most tables in Drupal 7.
Drupal 8 introduces a new element '#type' => 'table', which comes with built-in, optional support for TableDrag and TableSelect, and which requires no more custom plumbing for most use-cases.
Note: The following conversion example shows both TableDrag and TableSelect in a single table for brevity, but they are usually not combined in a single table.
Drupal Form Element Reference
Drupal core provides a couple dozen different input #type elements that can be added to forms. This includes one for every standard HTML5 input element, and some Drupal-specific ones that encapsulate more complex interactions like uploading files. But how can you know what elements exist? Where do you find information about what Render API properties each element uses?
How to change an existing Drupal form
Changing an existing form is one of the first things that new Drupal developers will learn how to do.
It is a natural extension from site building, where you might need to change one thing on a form created by a core or contributed module.
One of the benefits of using the Form API to construct forms is that any module can alter any other module's form.
In this tutorial, you are going to learn how to alter a Drupal form.
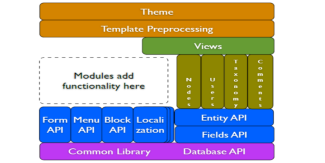
Render API overview and Render Element
The main purpose of Drupal's Theme system is to give themes complete control over the appearance of the site, which includes the markup returned from HTTP requests and the CSS files used to style that markup.
In order to ensure that a theme can completely customize the markup, module developers should avoid directly writing HTML markup for pages, blocks, and other user-visible output in their modules, and instead return structured "render arrays" (see Render arrays below).