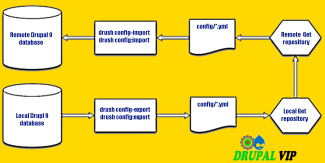
Drupal Service
Displaying 1 - 3 of 3Simple Configuration API
The configuration API comes in two flavors - the (simple) Config API and the Configuration Entity API.
The key difference is that the Config API is the singleton use case.
A singleton is where there can be only a single instance of this configuration.
A good example would be the site's name.
The Configuration Entity API should store multiple configuration sets - for example, node types, views, vocabularies, and fields.
Creating And Using URLs And Links Programmatically
When building a new module, you always get to the point where you want to use the routes you have been created, or other URLs, so if you find yourself always looking for how to print out a URL, this article is for you.
The difficulty is that finding or printing out a URL is very contextual and there is more than one way to get or use this information in Drupal.
You might have a node object that you need to convert into a fully qualified path, or you want to print out the path of a route, each of which has different approaches.
How to keep your session data
Sometimes you need to temporarily store information per same user, which means handling his session data, in previous version of drupal it was easy and more like handling it in PHP programming, but with drupal 8, since the desire was to do everything in OOP strategy it changed.
This article will review some of the options to handle session date which are available on drupal8.
First lets remember how it was done with drupal7: using the $_SESSION in module file during the hooking implementation
In Drupal 8 there's two services to handle session data: