Fetching data using inbuilt fetch API
All modern browsers come with an inbuilt fetch Web API, which can be used to fetch data from APIs.
In this tech article, I will to show you how to do fetching data from the JSON Server APIs.
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
Code Snippet
import React, { useEffect, useState } from "react"
const UsingFetch = () => {
const [users, setUsers] = useState([])
const fetchData = () => {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(response => {
return response.json()
})
.then(data => {
setUsers(data)
})
}
useEffect(() => {
fetchData()
}, [])
return (
<div>
{users.length > 0 && (
<ul>
{users.map(user => (
<li key={user.id}>{user.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</div>
)
}
export default UsingFetchHow to pass a Function as a Prop
Props or properties in react are a functional argument by which different components communicate with each other.
Props is just a data/information that allows us to pass in JSX tags.
With the help of props, we can pass values like JavaScript objects, arrays or functions, etc.
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
Code Snippet
import React from "react";
function Course(props) {
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>{props.courseName}</li>
</ul>
</div>
)
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Guvi Courses</h1>
<Course courseName="Full Stack Development" />
</div>
);
}
export default App;The node access system
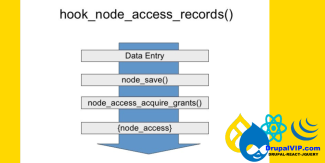
All node access modules are queried using hook_node_grants() to assemble a list of "grant IDs" for the user.
This list is compared against the table.
If any row contains the node ID in question (or 0, which stands for "all nodes"), one of the grant IDs returned, and a value of TRUE for the operation in question, then access is granted.
Note that this table is a list of grants; any matching row is sufficient to grant access to the node.
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
entityQuery intro and examples
A node can include a few fields.
Every field is a table in the database.
So If I need to find a specific node, doing it with SQL means doing complicated queries, which might have few joins and many conditions, The Drupal platform created a simpler way to deal with it: EntityQuery
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
Code Snippet
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('type', 'page')
->condition('field_some_field', 14)
->accessCheck(TRUE);
$results = $query->execute();Drupal module info file
Drupal uses .info files to store metadata about themes and modules.
For modules, the .info file is used for:
- Rendering information on the Drupal Web GUI administration pages;
- Provide criteria to control module activation and deactivation;
- Notifying Drupal about the existence of a module;
- Specifying the module's dependencies on other Drupal projects
for general administrative purposes in other contexts.
This .info file is required for the system to recognize the presence of a module.
Code Snippet
name: Hello World Module
description: Creates a page showing "Hello World".
package: Custom
type: module
core_version_requirement: ^9.4 || ^10
dependencies:
- drupal:link
- drupal:views
- paragraphs:paragraphs
- webform:webform (>=6.1.0)
test_dependencies:
- drupal:image
configure: hello_world.settings
configure_parameters:
pluginId: hello_world_plugin
php: 8.0
hidden: true
required: true
# Set the module lifecycle status deprecated
lifecycle: deprecated
lifecycle_link: https://www.drupal.org/node/3223395#s-aggregator
# Note: do not add the 'version' or 'project' properties yourself.
# They will be added automatically by the packager on drupal.org.
# version: 1.0
# project: 'hello_world'Open Ajax Modal Dialog from Controller
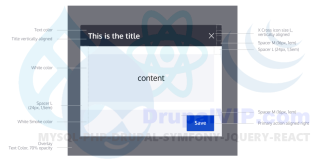
Dialogs are often called dialog boxes, modal windows, or pop-up windows.
Whatever you call them, they are a quick and easy way to display additional information without reloading the entire page.
Dialog boxes can display just some static text, any node or form of your page, a views page, or any custom markup you'll feed them.
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
Code Snippet
public function requestResidenceUpload(Request $request): AjaxResponse {
$arg = $request->get('arg1');
// Add an AJAX command to open a modal dialog with the form as the content.
$response = new AjaxResponse();
$modal_form = $this->formBuilder->getForm('Drupal\mymodule\Form\MyForm', $arg);
$response->addCommand(new OpenModalDialogCommand('Upload', $modal_form, ['width' => 600, 'height'=>600]) );
return $response;
} Introduction to Web Accessibility
When websites and web tools are properly designed and coded, people with disabilities can use them.
However, many sites and tools are currently developed with accessibility barriers that make them difficult or impossible for some people to use.
Making the web accessible benefits individuals, businesses, and society.
International web standards define what is needed for accessibility.
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
Success Message After Submitting Form
In building a custom form you must keep in mind a few issues:
elements, functionality, and response for best user experience
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
Code Snippet
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$this->logger('user')->notice('Deleted %ip', ['%ip' => $this->banIp,]);
$this->messenger()->addStatus($this->t('The IP address %ip was deleted.', [ '%ip' => $this->banIp, ]));
$form_state->setRedirectUrl($this->getCancelUrl());
}How To Attach Library To A Specific Content Type
If you need to upload a library with a module during its operation, in Drupal it's called attaching file.
Attaching a library can be done in several ways depending on your needs.
Remember that the library is always registered by its module or theme name followed by the library name.
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
Code Snippet
function rwcenter_page_attachments(array &$attachments) {
$attachments['#attached']['library'][] = 'rwcenter/content';
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node') ?? \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node_preview');
if (is_null($node)) {}
else {
if ($node->getType()=='rwcenter') {
$attachments['#attached']['library'][] = 'rwcenter/content';
}
}
}Drupal 7 to Drupal 9 in an hour, is it possible
Countless blog posts have been written about migrating from Drupal 7 to 8/9/10.
Some recommend how to begin breaking down this rather overwhelming endeavor into manageable pieces.
Others provide concrete technical recommendations for very specific Drupal 7 setups.
DrupalVIP technical notebook & support
Messenger Api: How to set message
Drupal set message was deprecated in Drupal 8.5 and will be removed before Drupal 9.
Time for a roundup of this new API and how to use it.
Code Snippet
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage('This is a regular message');
\Drupal::messenger()->addStatus('This is a status message, meaning status is OK or successful (green).');
\Drupal::messenger()->addError('This is an error message (red)');
\Drupal::messenger()->addWarning('This is a warning message (orange)');Tag-Based Caching IN Drupal Views
tag-based caching in Drupal views
Tag-based caching enhances the performance of your website by allowing fine-grained invalidation of cached content.
This is particularly important for dynamic websites where content changes frequently, but you still want to leverage caching to reduce server load and improve page load times.
REACT: Controlled or Uncontrolled components
The form is one of the most-used HTML elements in web development.
Since the introduction of React, the way forms have been handled has changed in many ways.
In React, there are two ways to handle form data in our components:
The first way is the Controlled Component:
We handle form data by using the state within the component to handle the form data.
The Second way is Uncontrolled Component:
We let the DOM handle the form data by itself in the component.
Code Snippet
Controlled Component
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
state = {
message: ''
}
updateMessage = (newText) => {
console.log(newText);
this.setState(() => ({
message: newText
}));
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<div className="container">
<input type="text"
placeholder="Your message here.."
value={this.state.message}
onChange={(event) => this.updateMessage(event.target.value)}
/>
<p>the message is: {this.state.message}</p>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}