Drupal Dictionary
#A #B #C #D #E #F #G
#H #I #J #K #L #M #N
#O #P #Q #R #S #T #U
#V #W #X #Y #Z
Total terms: 196
A: 17 terms; B: 11 terms; C: 27 terms; D: 28 terms; E: 2 term; F: 10 terms; G: 3 terms;
H: 5 terms; I: 6 terms; J: 1 term; K: 0 terms; L: 6 terms; M: 8 terms; N: 4terms;
O: 2 term; P: 9 terms; Q: 3 terms; R: 12 terms; S: 7 terms; T: 12 terms; U: 10 terms;
V: 5 terms; W: 6 terms; X: 0 terms; Y: 0 terms; Z: 2 terms;
last update: March 24
- A -
Account -
Users create accounts by registering on the site or receiving log-in information (username and password) from a site administrator.
When the user is logged in under that account, any content he or she creates in the future will be associated with them.
Action -
A function that operates like a stored procedure.
The function parameters, if any, are stored in the database and the function is executed by retrieving these stored parameters and calling the function.
Actions -
Drupal core module that allows configuration of tasks to be executed in response to events.
ADO -
Api.drupal.org. API reference site for Drupal developer's documentation.
Aggregator -
The Aggregator module is a feed reader that is included in Drupal Core.
When enabled, the Aggregator module can fetch syndicated content from other websites.
It gathers and displays syndicated content (RSS, RDF, and Atom feed) from external sources.
AJAX -
AJAX stands for Asynchronous JavaScript And XML.
In a nutshell, it is using the XMLHttpRequest object to communicate with servers.
Ajax is the process of dynamically updating parts of a page's HTML based on data from the server without requiring a full page refresh.
You can find events triggering Ajax requests all over Drupal, for example when selecting Views filters, Views pagers, or forms widgets like autocomplete fields.
AJAX Callback Event -
The Ajax event is defined in the form element, and the callback is the function which will be activate within that event
'#ajax' => [
'callback' => '::myAjaxCallback', // don't forget :: when calling a class method.
//'callback' => [$this, 'myAjaxCallback'], //alternative notation
'event' => 'change',
],
Ajax Forms -
Using AJAX callbacks to dynamically react on user input, alter form elements, show dialog boxes, or run custom Javascript functions.
Alias -
A user-friendly name to replace the internal path that the system assigns to a URL on the site.
For example, you might assign an alias of /about to the About page on your site, to replace the internal path /node/5.
This would give the page a URL of http://example.com/about instead of http://example.com/node/5. read more.
Annotations -
Annotations are like metadata descriptions above the class definition.
From Drupal 8 the Drupal framework is doing a lot of use with annotation, almost in every plugin.
This lets classes register themselves as plugins and describe their metadata. read more.
Anonymous -
A visitor to a Drupal website who is not currently logged in.
Drupal considers any such visitor as the anonymous user, with the user ID 0, and belonging to the anonymous user role.
Apache Solr -
Solr is an open-source enterprise-search platform, written in Java. Its major features include full-text search, hit highlighting, faceted search, real-time indexing, dynamic clustering, database integration, NoSQL features, and rich document handling. Providing distributed search and index replication, Solr is designed for scalability and fault tolerance.
API -
An application programming interface (API) is a particular set of rules (“code”) and specifications that software programs can follow to communicate with each other. Within Drupal, there is the API Reference which contains documentation for developers.
There is also a Form API and Field API
Argument -
A section of the path for a page on a Drupal website. In the path /node/937, the first argument is “node”, and the second is “937”.
Some modules, most notably Views, allow the use of “wildcard” arguments that allow a particular page to vary depending on context.
Article -
One of two content types that are enabled in the standard installation profile.
Articles are used for time-sensitive content like news, press releases, or blog posts.
This content type is called "Article" in Drupal 7 and later, and "Story" in earlier versions of Drupal.
Activity Tracker -
Enables tracking of recent content for users.
The Activity Tracker core module displays a site's most recently added or updated content.
The Activity Tracker module also provides user-level tracking, which allows you to follow the contributions of specific authors.
ATS -
Applicant Tracking System (ATS)
- B -
Basic page -
One of two content types that are enabled in the standard installation profile. Typically basic pages are used for static content that can (but are not required to) be linked to the main navigation bar. This content type is called "Basic page" in Drupal 7 and later, and "Page" in earlier versions of Drupal.
Base theme -
A Base theme is a well-written set of CSS and template files that a theme developer can make use of in a new custom theme. Theme developers can make sub-themes to override the default base theme. Some of the popular base themes include Zen, Omega and AdaptiveTheme
BigPipe -
Sends pages using the BigPipe technique that allows browsers to show them much faster. BigPipe was conceived at Facebook as a solution to load dynamic pages quickly. It's a way of loading various sections of your web page in parallel so end-users don't have to wait for the DOM to be completely ready to start interacting with the website.
BLOB -
Binary Large Object. A collection of binary data stored as a single entity in a database management system.
Block -
The boxes are visible in the regions of a Drupal website. some blocks are generated on-the-fly by various Drupal modules, but they can be created in the administer blocks area of a Drupal site. See the documentation for more information on blocks.
BoF -
Birds of a Feather (BoF) refers to an informal discussion group. Unlike special interest groups or working groups, BoFs are informal and often formed in an ad-hoc manner. BOF meetings are common adjuncts to planned "sessions" at Drupal camps and at DrupalCons
Book -
A set of pages tied together in a hierarchical sequence, perhaps with chapters, sections, subsections, and so on. You can use books for manuals, site resource guides, Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs), or whatever you’d like. To use books, enable the core Book module.
Breadcrumb -
The set of links, usually near the top of the page, shows the path you followed to locate the current page. For example, it might show Home > Macadamia Nuts > Current Events > News Articles, meaning that you started at the home page, clicked on “Macadamia Nuts” in the menu, then select “Current Events” in the sub-menu, and finally selected, “News Articles.” The term breadcrumb is borrowed from Hansel and Gretel, who left crumbs of bread along their path so they could find their way back out of the forest.
Breakpoint -
Breakpoints are used to separate the height or width of browser screens, printers, and other media output types into steps. A responsive site adjusts its presentation at these breakpoints. See “Concept: Responsive Image Styles” for more information.
Branch Maintainers -
See core committers
Bundle -
A specific implementation of an entity type. For example, the node entity type has bundles called content types. Default node bundles are “page” and “article”.
- C -
Cache -
The core Drupal cache stores assembled pages and blocks for anonymous visitors in the cache tables in the database. Other popular Drupal caching options include boost, Memcache, and authcache.
Callback -
The mechanism for registering a path so that the correct function is fired when the URL is accessed. They are not shown in the menu. For understanding callbacks see Drupal’s page serving mechanism.
Camp -
A camp is a one to two-day event that focuses on many aspects of Drupal in one location. Its focus is knowledge sharing amongst the community. Essentially, you’re getting the community together to do some community training. See Organizing Drupal Camps for more information.
CCK -
Content Construction Kit. Permits site developers to define custom fields and content types. A variety of extension modules to CCK exist permitting specialized field definitions such as images, dates, and computed values. Originally contrib, features split into separate modules and moved to core in Drupal 7 and 8.
Child -
Objects can have hierarchical relationships, such as menu items, book pages, taxonomy terms, and so on. A “child” menu item, for example, is nested under another menu item, which is referred to as the “parent” menu item.
CI/CD
![]() In software engineering, CI/CD or CICD is the combined practice of continuous integration and continuous delivery or, less often, continuous deployment.
In software engineering, CI/CD or CICD is the combined practice of continuous integration and continuous delivery or, less often, continuous deployment.
They are sometimes referred to collectively as continuous development or continuous software development.
CI/CD comprises of continuous integration and continuous delivery or continuous deployment. Put together, they form a “CI/CD pipeline”—a series of automated workflows that help DevOps teams cut down on manual tasks:
- Continuous integration (CI) automatically builds, tests, and integrates code changes within a shared repository; then
- Continuous delivery (CD) automatically delivers code changes to production-ready environments for approval; or
- Continuous deployment (CD) automatically deploys code changes to customers directly.
CKEditor -
Modern JavaScript rich text editor with a modular architecture. Its clean UI and features provide the perfect WYSIWYG UX ❤️ for creating semantic content. module for Drupal is available for drupal7 later versions is part of the core, this module is used in the multi-line text editing field. read more
Clean URL -
A URL that does not contain code. By default, Drupal uses and generates URLs for your site’s pages that look like “http://www.example.com/?q=node/83.” By enabling clean URLs this will be rewritten to “http://www.example.com/node/83”.
CMS -
Content Management System (CMS), in the context of a website, serves as a collection of tools that allow the creation, modification, organization, search, retrieval, and removal of information. Besides Drupal, other CMSs include WordPress and Joomla!.
Code Freeze -
The date at which no new features can go in the next version of Drupal unless specific dispensations have been made by the core committers (even then, only when the impact on other systems is minimal). At code freeze, the focus in Drupal core shifts to bug fixing and usability improvements. It is the time when contributed module developers can begin working on updating their code to work with the next version of Drupal.
Commit -
Process of applying a patch to code and pushing it on the Git Server, so that this change is visible and downloadable by everybody. In Git terms actually do not involve the push part, but in the Drupal community generally, this is included.
Composer -
A dependency manager for PHP used by drush, the Symfony framework, and Drupal 8. The preferred means of installing many Drupal projects. See Drupal developer documentation for more details.
Configuration -
Information about your site that is not content, and is meant to be more permanent than state information, such as the name of your site, the content types and views you have defined, etc
Configuration Management -
Introduced with Drupal 8 as a way to keep track of the important details as you configure and revise your site. Drupal 8 comes with a file system-based configuration management system, which provides tools for transporting configuration changes such as new content types, fields, or views from a development server to a production server (or similar). It even lets you use version control for your configuration. Save your config data from the database to files. Learn more about basic configuration management concepts.
Content -
The text, images, and other information on a website. Besides nodes, there is more content on a typical Drupal site, such as comments and file attachments.
Content Construction Kit -
See: CCK.
Content-type -
Every node belongs to a single “node type” or “content-type”, which defines various default settings for nodes of that type, such as whether the node is published automatically and whether comments are permitted. Common "Content Types" that just about any website would have include: blog posts and pages. Content types can have different fields and modules can define their own content types. The core Drupal Book and Poll modules are two examples of modules that define content types.
Context -
Multiple meanings depending on use.
- Context: A popular contrib module that allows you to vary the theme, block layout, menus, etc. based on conditions such as the content type, current user, etc. It is frequently used to provide variety in the user experience across different sections of your site.
- A key concept of the ctools module was taken from Panels. Contexts provide a consistent wrapper API for various objects (nodes, users, etc.). This greatly simplifies the coding necessary to make user interface functionality aware of the objects that could influence its behavior.
Contextual Link -
A link to an administrative page for editing or configuring a feature of the site, shown in the context where that feature is displayed. read more .
Contrib -
Contributed. Modules or themes that are not part of the core Drupal product. Contributed modules and themes are available for separate download from the modules and themes sections of Drupal.org downloads. These are separate from the Drupal “core”, although over time they can become part of it. Similar concepts exist in other software and are sometimes called “plugins”, “add-ons” or “extensions”.
COPE -
Create Once, Publish Everywhere. COPE is really a combination of several other closely related sub-philosophies, including:
- Build content management systems (CMS), not web publishing tools (WPT)
- Separate content from display
- Ensure content modularity
- Ensure content portability
Core -
The files and modules included with the Drupal project download.
Core Committers -
Drupal developers that review proposed changes to the Drupal core and maintain code. They are the only ones who have to write access to the core Git repository.
Core Contributor -
Developers who contribute code patches or documentation for the Drupal core. Contributions are peer-reviewed and then evaluated by the core committers.
Core Maintainers -
See core committers
Critical Path -
The code that is run when serving a cached page.
Cron -
A command scheduler that executes commands or scripts (e.g. scripts to backup a database) automatically at specified time and date intervals. Drupal uses a “cron job” to perform periodic tasks that help Drupal to run smoothly and efficiently.
index #A #B #C #D #E #F #G #H #I #J #K #L #M #N #O #P #Q #R #S #T #U #V #W #X #Y #Z
- D -
D6 -
Drupal 6. Any version 6 of Drupal, including all minor versions 6.x.
D7 -
Drupal 7. Version 7 of Drupal, which includes any minor version, e.g. Drupal 7.0, Drupal 7.23
D8 -
Drupal 8. Version 8 of Drupal, which includes any minor version, e.g. Drupal 8.0, Drupal 8.1. D8 can also refer to beta versions, e.g. Drupal 8.0.0-beta10, or versions still in the development stage, e.g. Drupal 8.x-dev
D9 -
Drupal 9. Version 9 of Drupal
DA -
Drupal Association. An organization dedicated to helping the open-source Drupal project flourish.
Database API -
Drupal's database abstraction layer provides a unified database query API that can query different underlying databases. It is built upon PHP's PDO (PHP Data Objects) database API and inherits much of its syntax and semantics. read more
Decoupled Content -
A decoupled content store splits the content of a website from how it is displayed on multiple independent systems. Decoupled sites are the logical evolution of splitting content from templates in the current CMS.
Delete Queries -
The delete query object uses a fluent API. That is, all methods (except execute()) return the query object itself allowing method calls to be chained. In many cases, this means the query object will not need to be saved to a variable at all. read more.
Delta -
An index for fields, blocks, etc., of the same type.
Devel -
Devel is a suite of modules that provides helper functions, admin pages, and additional development Drush commands to use during development.
On your development site, you can use Devel to generate dummy(example) content and examine service containers, routes, and events.
Inside your PHP code Devel adds new PHP functions to output various messages, directly on the page in question. Use these messages to help debug your code. Devel
Development tools -
Use these development tools to help you create Drupal sites faster and with less effort. If you have a favorite Drupal tool that is not listed, please update us by note/comment. https://www.drupal.org/docs/develop/development-tools/development-tools-overview
Display mode -
In Drupal 8, "Display Modes" is an area in the core interface under "Structure" that comprises view modes and form modes, both of which are used to create custom displays of entities and their edit forms.
Distribution -
A single downloadable archive containing Drupal core, contributed modules, themes, and pre-defined configuration.
A distribution provides site features and functions for a specific type of site.
They make it possible to quickly set up a complex, use-specific site in fewer steps than if installing and configuring elements individually.
An index of distributions is available on the Distributions page.
DO, D.O. -
Drupal.org. The website of Drupal “(where you are right now)”.
Docker -
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. With Docker, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications. By taking advantage of Docker’s methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code quickly, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production. https://docs.docker.com/
Dos2Unix -
The Drupal coding standards specify Unix-style line endings.
If you inherit code that uses a different convention, the easiest tool to correct the code is dos2unix.
If you develop on Linux, you will probably find it installed, or if not you can probably install it from your distribution's repository.
To correct all code files in a directory and its subdirectories, cd to the top directory and use the CLI command find -name \*|xargs dos2unixhttps://waterlan.home.xs4all.nl/dos2unix.html
Druml -
Druml is an Open Source project that helps to manage hundreds of Drupal sites in the same doc root.
Druml is a set of bash scripts. Although Druml sounds similar to Drush, it is not a replacement for Drush, instead, it is an addition to Drush and it uses Drush a lot.
It also works nicely with Acquia Cloud Platform and there are some specific Acquia Cloud commands.
Landing page: http://www.usedruml.com/
Git page: https://github.com/georgetown-university/druml
Drupal Code Generator -
A simple command-line code generator for Drupal. https://github.com/Chi-teck/drupal-code-generator
Drupal Console -
The Drupal Console is a suite of tools that you run on a command line interface (CLI).
A tool to generate boilerplate code, interact with and debug Drupal.
Drupal Console takes advantage of the Symfony Console and other well-known third-party components like Twig, Guzzle, and Dependency Injection among others. https://drupalconsole.com/
Drupal Core -
The files, themes, profiles, and modules are included with the standard project software download.
Drupal VM -
Drupal development environments for fast, quick, and easy to build, and introduces developers to the wonderful world of Drupal development on virtual machines or Docker containers (instead of crufty old MAMP/WAMP-based development). download VM environment.
DrupalCon -
The semi-annual conference is dedicated to gathering Drupal practitioners. It alternates between a North American location and a European location.
Druplicon -
The Drupal mascot. It is a neologism formed by joining the words “Drupal” and “icon”.
Drush -
Short for "Drupal shell". A command-line shell and scripting interface for Drupal. Full details are on the Drush GitHub page.
DX -
Drupal Developer Experience.
DXP -
Digital Experience Platform, A DXP gives organizations tools to gather comprehensive, cross-channel data to understand their customers, and then incorporate these lessons into the creation, management, and delivery of content.
Dynamic Queries -
Dynamic queries refer to queries that are built dynamically by Drupal rather than provided as an explicit query string. All Insert, Update, Delete, and Merge queries must be dynamic. Select queries may be either static or dynamic. Therefore, "dynamic query" generally refers to a dynamic Select query. read more
index #A #B #C #D #E #F #G #H #I #J #K #L #M #N #O #P #Q #R #S #T #U #V #W #X #Y #Z
- E -
Entity -
Any defined chunk of data in Drupal. This includes things like nodes, users, taxonomy terms, files, etc. Contributed modules can define custom entities. Each entity type can have multiple bundles.
Extend -
The new tab menu for the list of Drupal modules (since Drupal 8)
- F -
FAPI -
Feature -
Drupal configuration is exported into code using the Features module. In Drupal 7, Features have become the standard way of exporting and versioning configuration that is stored in the database so that it can be moved from development to QA to production in a repeatable manner.
Field -
Elements of data that can be attached to a node or other Drupal entities. Fields commonly contain text, terms, or an image.
Field Formatter -
Configuration that defines how the data in a field is displayed. For example, a text field could be displayed with a prefix and/or suffix, and it could have its HTML tags stripped out or limited.
Filter -
A tool for stripping out HTML, PHP, JavaScript, and other undesirable elements from the content before pages are displayed.
Other filters add formatting and features such as smilies.
It is possible to create custom filters that allow or forbid only those tags you wish.
More information is available on the Text Filters and Input Formats page.
Flag -
Using the flag module, any number of customizable "flags" may be added to any entity, e.g. for bookmarking, marking something as important, or as spam, marking users as friends, or flagging issues on Drupal.org.
Foobar -
A common placeholder name, e.g. for names of variables (“$foobar”) or functions (“foo_bar()”).
Fork -
A copy of source code from one software package that receives independent development, thus creating a distinct piece of software.
Form Mode -
A form mode is a way to customize the layout of an entity's edit form.
In Drupal 8 this is located under Structure > Display Modes.
FOSS -
Acronym for Free and Open Source Software, meaning software that is developed by a community of people and released under a non-commercial license
- G -
GDO -
Groups.drupal.org. The site serves the Drupal community by providing a place for groups to organize, plan and work on projects.
Real-world local user groups in particular are encouraged to setup their online presence at GDO.
Git -
A version control system used by Drupal code contributors to coordinate their individual code changes.
Git records everyone’s changes to a given project in a directory tree called a git repository.
For more information, see the Git documentation.
GUI -
Graphical user interface.
A program interface that takes advantage of the computer’s graphics capabilities to make the program easier to use.
- H -
Handler -
handler refers to a class that takes care of field display, sorting, filtering, contextual filtering, or relationships.
HEAD -
The current development version of core or a module.
Headless Drupal -
A Decoupled Drupal CMS that architect to be activated more on the server side and less on the client side, transferring all data via API requests. within this case, the information is being presented via the client application and not the Drupal templates.
Hook -
A PHP function is named foo_bar(), where “foo” is the name of the module (whose filename is thus 'foo.module') and “bar” is the name of the hook. Each hook has a defined set of parameters and a specified result type. See also the theme hook.
Human Readable -
Also a user-friendly name. The text string is used to identify a resource as displayed in the user interface, as opposed to the machine name used for internal purposes of the computer program.
HRIS -
Human Resource Information System (HRIS)
- I -
i18n -
Numeronym for internationalization, replacing the 18 middle letters with “18”. Internationalization refers to enabling translations and other-language support (including alternate character sets and right-to-left rendering) in computer systems.
IAAS -
Infrastructure As A Service (IAAS) is means of delivering computing infrastructure as on-demand services. It is one of the three fundamental cloud service models. The user purchases servers, software data center space, or network equipment and rent those resources through a fully outsourced, on-demand service model. It allows dynamic scaling and the resources are distributed as a service. It generally includes multiple-user on a single piece of hardware.
Insert Queries -
Insert queries must always use a query builder object. Certain databases require special handling for LOB (Large OBject, such as TEXT in MySQL) and BLOB (Binary Large Object) fields, so a layer of abstraction is required to allow individual database drivers to implement whatever special handling they require.
The execute command returns the last insert ID of the query if one exists. If the query was given multiple sets of values to insert, the return value is undefined. If no fields are specified, this method will do nothing and return NULL. That makes it safe to use in multi-insert loops. read more
Input Format -
A tool for defining the processing that happens to user-entered text before it is shown in the browser. Usually, different user roles are given permission to use different input formats depending on how much they are trusted. For those roles, the input format may often be available as an option that shows up underneath the body of a node edit form. For more information, see the Text Filters and Input Formats documentation.
IRC -
Internet Relay Chat. A network protocol that allows people to chat in real time over the Internet. Drupal discussions are often going on in The Drupal IRC Channels
Issue -
A unit of work to accomplish an improvement in a data system. An issue could be a bug, a requested feature, a task, missing documentation, and so forth. The Drupal community uses the issue queue to work as a team. If you need help with a specific project, whether it is a module or theme, you should go to the issue queue.
- L -
L10n -
Numeronym for localization, replacing the 10 middle letters with “10”.
LAMP -
Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP.
LAMP is an interoperable group of open-source computer programs that form the most common environment to run Drupal on.
Legacy Code -
A version of Drupal that is no longer supported.
The term can also mean code inserted into modern software for the purpose of maintaining an older or previously supported feature.
LOB -
Large OBject, MySql field type which stores binary object with data
Log -
A list of recorded events. A log may contain usage data, performance data, errors, warnings, and operational information.
Drupal’s events are logged by the modules dblog and Syslog.
Library -
A library of code from a third party. libraries is a module that will help you manage and load these.
- M -
Machine Name -
Also machine-readable name. The text string is used by the computer to identify a resource, as opposed to the human-readable name shown in the user interface.
Maintainer -
A single community person who is responsible for the module also has the right to commit a patch into the module. Can be multiple people per module.
Menu -
In Drupal, the term refers both to the clickable navigational elements on a page and to Drupal’s internal system for handling requests. When a request is sent to Drupal, the menu system uses the provided URL to determine what functions to call.
Microservices - 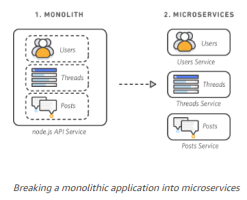
In software engineering, microservice architecture is a variant of the service-oriented architecture structural style.
It is an architectural pattern that arranges an application as a collection of loosely coupled, fine-grained services, communicating through lightweight protocols
Migrate -
Moving content from other sources into Drupal or from Drupal 6 or Drupal 7 into Drupal 8. See Introduction to migrate D6 to D8
Module -
Code that extends Drupal features and functionality (but doesn't provide the HTML markup or styling of a theme). Drupal core comes with required (pre-installed) modules and some of which are optional. Thousands of non-core or “contrib” modules are listed in the project directory.
Module Builder -
A module that auto-generates a skeleton or "scaffolding" for a module, along with hints on how to fill them in. Useful for newbie developers to learn how Drupal code works, and seasoned developers who are too lazy to look up what arguments a function has to take. https://www.drupal.org/project/module_builder
Multi-site -
A feature of Drupal that allows one to run multiple websites from the same Drupal codebase. See Multi-site - Sharing the same code base
- N -
Next.js -
Next.js provides a TypeScript-first development experience for building your React application.
It comes with built-in TypeScript support for automatically installing the necessary packages and configuring the proper settings.
NID -
Node ID. The unique identifier for each node. It can be found in the path to the node.
For example, a node with the path, “http://drupal.org/node/937”, has a node ID of “937”.
Node -
A piece of content in Drupal, typically corresponding to a single page on the site, that has a title, an optional body, and perhaps additional fields. Every node also belongs to a particular content type, and can additionally be classified using the taxonomy system.
Examples of nodes are polls, stories, book pages and images.
Node Type -
See content type.
- O -
Object Oriented Programming (OOP) -
The focus of object-oriented programming is to break down a programming task into objects that expose behavior (methods) and data (members or attributes) using interfaces.
The most important distinction between procedural and object-oriented programming is that procedural programming uses procedures to operate on data structures, object-oriented programming bundles the two together so an "object", which is an instance of a class, operates on its "own" data structure.
Object Interface -
Object interfaces allow you to create code that specifies which methods a class must implement, without having to define how these methods are implemented.
Interfaces share a namespace with classes and traits, so they may not use the same name.
Interfaces are defined in the same way as a class but with the interface keyword replacing the class keyword and without any of the methods having their contents defined.
- P -
PAAS -
Platform As A Service (PAAS) is a cloud delivery model for applications composed of services managed by a third party. It provides elastic scaling of your application which allows developers to build applications and services over the internet and the deployment models include public, private and hybrid.
Page -
See Basic Page People also use the word "page" to mean a web page (i.e., a page you get to by navigating to a specific URL on a website).
Parent -
See child
Patch -
A small piece of software designed to update or fix problems with a computer program or its supporting data. This includes fixing bugs, replacing graphics, and improving usability or performance. For more information, see the patch documentation.
Path -
In Drupal terms, a unique, last part of the URL for a specific function or piece of content. For instance, for a page whose full URL is "http://example.com/?q=node/7", the path is “node/7”. Drupal can use clean URLs if the Path module is enabled, which would change the full URL in this example to "http://example.com/node/7" the path would still be “node/7”.
Permission -
In Drupal, permission is a tool for controlling access to content creation, modification and site administration at the application level. Administrators assign permissions to roles (such as "Administrator", "Authenticated User" and "Anonymous User"), then assign users to those roles. The first user of a Drupal site (User1) automatically receives all permissions. In operating systems like UNIX, permissions are security settings restricting or allowing users to access information or perform certain functions at the operating system level. In the case of files on UNIX systems, there are three types of permissions: read, write, and execute.
Plugin API -
Plugins are grouped into plugin types, each generally defined by an interface. Each plugin type is managed by a plugin manager service, which uses a plugin discovery method to discover provided plugins of that type and instantiate them using a plugin factory. read more
Procedural Programming -
The focus of procedural programming is to break down a programming task into a collection of variables, data structures, and subroutines. The most important distinction between procedural and object-oriented programming is that procedural programming uses procedures to operate on data structures, object-oriented programming bundles the two together so an "object", which is an instance of a class, operates on its "own" data structure.
Published -
The state of a node that can be viewed by visitors to the website. To easily hide nodes from the public (i.e. anonymous role), go to the add/edit form of the node and uncheck the “Published” select box. This effectively unpublishes the node.
- Q -
Query -
Defines the entity query for entities stored in a key-value backend. read more about the Query class
Quota -
Represents a quota for disk space. read more about the Quota class
Queue -
A job management technique. Jobs waiting in a line (queue) are usually processed on a first-in, first-out basis or by priority if specified.
The Drupal community uses the issue queue to work as a team.
If you need help with a specific project, whether it is a module or theme, you should go to the issue queue.
- R -
React -
JavaScript library for web and native user interfaces, React is a library. It lets you put components together, but it doesn’t prescribe how to do routing and data fetching.
learn and api reference
React Component -
React component is a JavaScript function that you can sprinkle with markup.
Reference Field -
A type of field that allows authors to create a relationship between an entity and one or more other entities.
For example, authors might "tag" an article with taxonomy terms using a Term Reference field. Other reference fields can be used to define other kinds of relationships (for example, between nodes and other nodes, or nodes and users). Depending on the Drupal version and/or contributed modules installed, these might be called Entity Reference, Node Reference, or User Reference fields.
Region -
Defined areas of a page where content can be placed.
Basic regions include Header, Footer, Content, Left sidebar, and Right Sidebar.
Different themes can define different regions so the options are often different per site.
Content is assigned to regions via blocks. They can be ordered by weight within regions to define the order in which they display.
Content with more negative weight, such as -10, will appear above content with a more positive weight, such as 1.
Render Array -
Render arrays are the basic building blocks of Drupal content. In Drupal 7, render arrays provide a structured way to programmatically alter content before it is displayed. Further details can be read on the Render Arrays documentation page.
Reroll -
Reimplementing of code on top of HEAD of a code repository, mostly because HEAD has changed. Learn more.
Responsive -
A site or theme is said to be responsive if it adjusts its presentation in response to the size of the browser screen, printer, or other media output type.
Roles -
A name for a group of users, to which you can collectively assign permissions. There are two predefined, locked roles for every new Drupal installation: authenticated user (anyone with an account on the site) and anonymous user (those who haven't yet created accounts or are not logged in). Additional roles can be created and users can belong to more than one. See users, permissions and roles.
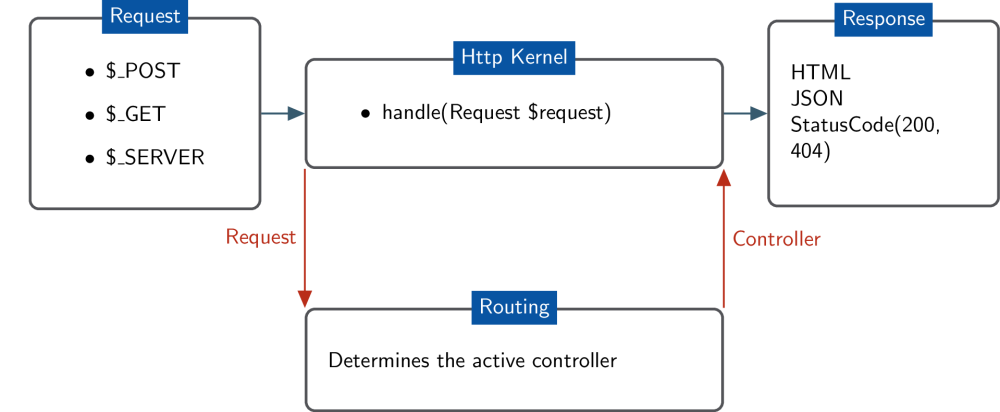
Routing -
The routing system will associate the path to a controller, while the menu system will make the item appear in the administration section.
Drupal's routing system works with the Symfony HTTP Kernel. However, you don't need to know very much about the Symfony HTTP Kernel to do basic route operations. Drupal 8's routing system is heavily based on Symfony's. Drupal's routing system can do everything Symfony's can (and more), and both use the same syntax to define routes. read more.
RSS -
Really Simple Syndication. A family of Web feed formats used to publish frequently updated content such as blog entries, news headlines or podcasts. An RSS document (which is called a “feed” “web feed” or “channel”) contains either a summary of content (“teaser”) from an associated website or the full text. RSS is one of the many ways of connecting a Drupal website with external sites, systems and data.
RTBC -
Reviewed and tested by the community. RTBC is one of the statuses given to issues in the issue queue.
RTL -
Right-to-left. Languages such as Arabic and Hebrew run from right to left across a written page, and need to do the same on a web browser. RTL support can be problematic in theme design, but is possible, as explained in the Drupal theme guide for RTL.
- S -
SAAS -
Software As A Service (SAAS) allows users to run existing online applications and it is a model software that is deployed as a hosting service and is accessed over Output Rephrased/Re-written Text the internet or software delivery model during which software and its associated data are hosted centrally and accessed using their client, usually an online browser over the web. SAAS services are used for the development and deployment of modern applications.
Schema -
A formalized array structure representing one or more database tables and their related keys and indexes. More information can be found in the Schema API.
SDLC -
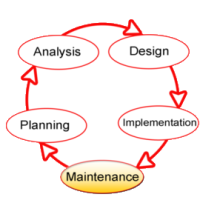
Systems development life cycle, In systems engineering, information systems, and software engineering, the systems development life cycle, also referred to as the application development life cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system.
Sprint -
A meeting where people meet gathers at a specific time to discuss and work on software development tasks. A code sprint is a typical element of a Drupal event.
Static Queries -
Static queries are common SELECT queries that use the query() method of a database connection object. Static queries are passed to the database nearly verbatim. read more
Story -
A content type that is defined in a default Drupal installation, is typically used for content that has a date associated with it, such as a news item. This content type's name was changed to Article in Drupal 7.
Symfony Components -
A set of decoupled and reusable components on which the best PHP applications are built, such as Drupal, Prestashop, and Laravel.
Symfony components in Drupal include:
HttpKernel and HttpFoundation ,EventDispatcher, ClassLoader, YAML, Routing, DependencyInjection, Twig, Process, Serializer, Validator, Translation, and many more.
The integration with Drupal started with Drupal8 and it's even much more robust.
- T -
Tag, Term -
An organizational keyword, known in other systems as categories or metadata. A term is a label that can be applied to a node. They are also known as tags.
Tar.gz -
Tape archive. A file format and the name of the program used to handle such files. Drupal projects are distributed in Zip and tar.gz formats. A *.tar.gz file is a combination of two technologies: Tar - creates the file and Gzip - compresses the file (similar to zip).
Taxonomy -
In Drupal, "Taxonomy" is the name of a powerful core module that gives your site the use of terms. In Drupal, these terms are gathered within vocabularies that the Taxonomy module allows you to create, manage and apply.
Teaser -
A short introductory sentence or paragraph about a piece of content informs readers about the subject of the content. By default, the first paragraph or two of the content is used (there is a setting for how much), usually with a link to the complete node.
Template -
A file to express presentation (vs. program logic). Templates are mostly written with a markup language like HTML with variables representing data provided to the template. The variables in templates substitute in values provided by a theme engine.
Testbot -
A continuous integration service for testing patches submitted to project issues on Drupal.org. These are maintained by the Drupal.org Infrastructure team.
Theme -
A collection of template files, configuration files, and asset files (JavaScript, CSS, images, fonts) which together determine the look and feel of a site. A theme contains elements such as the header, icons, block layout, etc. Drupal modules define themeable functions which can be overridden by the theme file. There are additional themes available in the themes section of downloads.
Theme Engine -
A set of scripts that interprets code and makes theming a site easier. These scripts take the dynamically generated content and output it to HTML. Drupal has three theme engines in addition to being able to write a theme that bypasses the theme engine. The default theme engine is PHPTemplate. There are additional theme engines for downloads.
Theme Hook -
An identifier is used by the calls to the theme() function to delegate rendering to a theme function or theme template. Modules that extend Drupal may declare their own theme hooks to allow them to control the markup of that module in their theme.
Theme hooks are distinct from API hooks, although similar in concept.
Trigger -
Defined by modules, triggers typically result from some characteristic change in an entity maintained by a module. Some examples of triggers are: deleting content, adding a comment that a user has logged in, or adding a term. In addition to the triggers provided by the Drupal core modules, triggers may be added by installing contributed modules.
Triage -
A new bug or issue is assigned a priority based on its severity, frequency, risk, and other predetermined factors, borrowed from medical term triage.
TypeScript -
TypeScript is a popular way to add type definitions to JavaScript codebases.
- U -
UID -
User ID. The unique identifier for each user. It can be found in the path to the user profile, e.g. “http://drupal.org/user/1”
Unpublished -
See published
Update -
Moving from one minor release to another, e.g. moving from Drupal 7.12 to Drupal 7.14. See Upgrading from previous versions.
Update Queries -
Update queries must always use a query builder object. Certain databases require special handling for LOB (Large OBject, such as TEXT on MySQL) and BLOB (Binary Large Object) fields, so a layer of abstraction is required to allow individual database drivers to implement whatever special handling they require.
The return value is the number of rows matched by the update query, including rows that actually didn't have to be updated because the values didn't change. read more
Upgrade -
Moving from one major release to another, e.g. moving from Drupal 7 to Drupal 8. See Upgrading from previous versions.
URL -
uniform resource locator. The address defines the route to locate an object on an Internet server. Generally, the syntax for a URL contains the scheme, hostname, port, path, and filename, e.g. http://www.drupal.org/node/937
User -
The user interacts with Drupal. This user is either anonymous or logged into Drupal through their account.
User 0 -
Anonymous user – anyone without an account or who has not logged in to the site. Although anonymous users don't have a profile, they still have a record in the user's table because they still can be assigned certain permissions (e.g. viewing comments or using the contact form).
User 1 -
The first user was created on installation (and thus with a UID of 1 in the database). Granted additional (all) permissions and referred to as the site maintenance account in Drupal 7.
UX -
User experience. An umbrella term refers to the overall experience and satisfaction a user has when using a website. It is important to note that this “includes only what the user perceives and not all that is presented.”
- V -
View -
In reference to the Views module above, a view is what is created when the site builder adds or creates a new view from the interface. Each view uses a table in the database as a "base table" to build a list of objects. The view by itself is an abstract wrapper of instructions that are inherited by each view display created within the view.
View Display -
In reference to the Views module above, view displays are created inside of a view to display the objects fetched by the view in different manners. For example, a view called "Blog Posts" might have view displays for "Top 5", "Most Recent", or "Posts by Author".
View Mode -
A view mode is a way to customize how an entity is rendered. Examples are 'Full Page', 'Teaser' or 'JSON'. In Drupal 8 this is located under Structure > Display Modes.
Views -
A module that allows site developers a graphical interface for creating lists of various Drupal entities; most notably users and nodes. Views permits the selection of specific fields to display, filtration against various attributes, choice of basic layout options (i.e. list, full entities, teasers, etc.), and other more advanced features. Many Drupal sites use Views extensively. In Drupal 8, the Views module is part of Drupal Core.
Vocabulary -
A vocabulary is a collection of terms. Click here to read more.
- W -
webpack -
Webpack is a static module bundler for modern JavaScript applications.
When webpack processes your application, it internally builds a dependency graph from one or more entry points and then combines every module your project needs into one or more bundles, which are static assets to serve your content from
read more
Weight -
Weights define the priority or order in which a function or hook is processed or a block/node is displayed (e.g. menu items). Lower weight values (-10) float to the top of lists, while heavier (+10) weights appear lower.
Widget -
A field API and CCK term are used to refer to the HTML form element used to collect the input for the field from the user.
WYSIWYG -
What You See Is What You Get. An acronym used in computing to describe a method in which content is edited and formatted by interacting with an interface that closely resembles the final product.
WebProfiler -
WebProfiler adds a toolbar at the bottom of every page and shows you all sorts of stats such as the amount of database queries loaded on the page, which services are used, and much more. https://www.drupal.org/project/webprofiler
Web Services -
A web service is a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network. In other words, a web service is any software that allows two or more programs (machine-to-machine) to exchange information and/or instructions (interoperable interaction) across the Internet or a local area network.
Drupal has two main web service technologies: HTTP web services, and REST web services.
- X -
- Y -
- Z -
Zebra Striping -
Alternating colors behind rows of data.
This is often used in tabular data where rows of data alternate background colors between white and a shade of gray.
Zip -
The zip file format is a data compression and archive format.
A zip file contains one or more files that have been compressed, to reduce file size.
Drupal core and modules are offered both in the zip and tar format.